News
July 2024
Biogenic polymers, biochar, peat moss harvesting
by Dorothee Scheuch (comments: 0)
New paludiculture newsletter

25/07/2024 Biogenic polymers and biochar - both can be related to paludiculture and are the subject of the latest issue of our newsletter. A look at the final report from MOORuse reveals that natural fibres from paludiculture are suitable as biogenic polymers in terms of sustainability, for example for injection moulding or 3D printing. In England, researchers are investigating whether biochar on paludiculture areas increases their carbon storage. We present the interactive online version of the Global Peatland Map and a legal report on rewetting in Germany and its obstacles. And of particular interest to land users: information on current funding for machinery and equipment for paludiculture!
We hope you enjoy reading the newsletter and would be pleased to receive feedback on it by e-mail to communication@greifswaldmoor.de.
Invitation: Conclusion "TyphaSubstrat"
by Dorothee Scheuch (comments: 0)
50% less peat is possible

22/07/2024 The aim of the three-year TyphaSubstrat project - harvesting and utilising cattail as an alternative substrate material for press pot soil in vegetable growing - was to develop a peat-reduced press pot soil with up to 50% less peat. At the final event on 5 September in Darmstadt, the project participants will present their results. These show: 50% peat reduction in pressed potting soil is possible! Presentations and dialogue in the morning at the Forschungsring e.V. in Darmstadt will be complemented by a tour of the practical tests in a vegetable nursery and a young plant farm near Mannheim. Detailed information on registration and the programme can be found here.
TyphaSubstrat focuses on cattail in a mixture with other peat substitute components such as sphagnum, green waste compost and wood for press pots, on which lettuce and vegetables are grown commercially. In addition, special technology for harvesting cattail was further developed in the project, and cattail raw material was analysed with regard to substrate properties, including pesticides and herbicides. By reducing the use of peat and utilising paludiculture biomass, TyphaSubstrat makes a dual contribution to the transformation towards climate-neutral use of wet peatlands (paludiculture) and demonstrates possibilities for sustainable substrate production. The proven suitability of cattail biomass as an alternative substrate offers the industry a new renewable raw material that can be produced regionally. A step towards a long-term secure and climate-friendly raw material supply and a contribution to peatland protection. TyphaSubstrat is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture via the Agency for Renewable Resources (Fachagentur für nachwachsende Rohstoffe e.V.).
Global Peatland Map 2.0!
by Dorothee Scheuch (comments: 0)
Now online
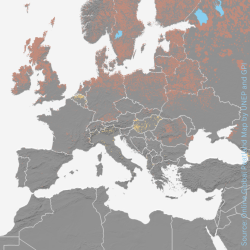
18/07/2024 The GMC's Global Peatland Map is now available online and interactive! It comprises eleven pages and covers a wide range of topics, such as the extent of peatlands per country, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity hotspots, peatlands in protected areas and sources of fire. A series of story maps “Peatlands in the Continents” will complement the Global Peatland Map 2.0. for a detailed look at regions offering key facts on peatland distribution, degradation and options for action. Visually intuitive, easy to navigate and beautifully designed, a first story map on Asian Peatlands can already be tried out.
The web version of the Global Peatland Map is based on data from the Global Peatlands Assessment from 2022, which summarized the best available scientific data to provide an overview of the state of peatlands worldwide. As a partner in the Global Peatlands Initiative, the GMC's map specialists created the online version in close cooperation with the World Environment Situation Room of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).